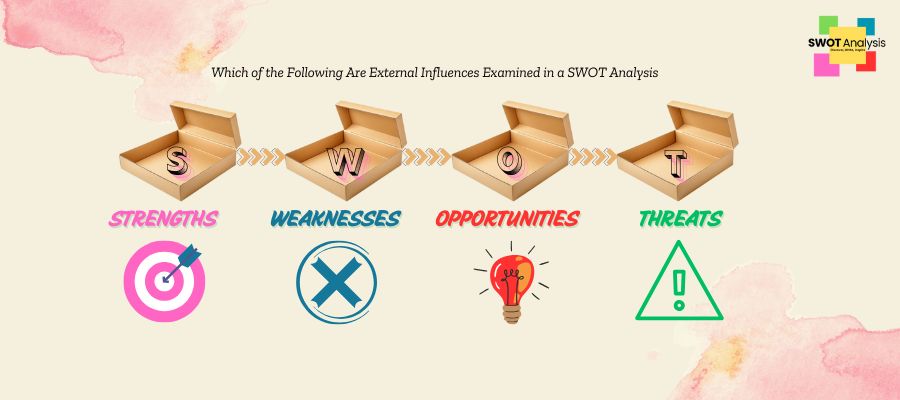
SWOT is Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. Finding and defining all this is done through a SWOT analysis. SWOT analysis can be used for specific initiatives within a particular functional area or for the entire firm or organization. SWOT analyses are most frequently performed at the corporate level to evaluate how closely a business is following its growth trajectories and meeting success benchmarks. However, they evaluate how well a specific project is doing in comparison to initial expectations.
What Is SWOT Analysis?
The strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of your business come in SWOT analysis. A SWOT analysis’s main objective is to assist organizations in fully comprehending every element involved in making a business choice.
Before making any kind of business decision—whether it’s about developing new strategies, updating internal protocols, brainstorming ideas for a change of direction, or modifying a plan in the middle of its implementation—do a SWOT analysis. With an emphasis on utilizing strengths and chances to defeat weaknesses and threats, use SWOT analysis for employees to identify suggestions and execution strategies.
Why SWOT Analysis is Essential for Businesses and Individuals.
For Businesses:
It plays a critical role in strategic planning. It provides a clear understanding of internal capabilities and external market conditions. Companies can use their competitive advantages with their strengths. Their weaknesses allow them to work on areas that need improvement. There are possible places for development and progress. The analysis’s threats highlight outside risks to the company. Making well-informed decisions is more easy after this analysis. When starting a new firm in a market or reorganizing operations, it is helpful. It helps the effective use of resources by businesses. This guarantees that resources and efforts are focused on return on investment.
For Individuals:
A SWOT analysis is equally valuable for people. It is useful in self-assessment. It helps people understand their strengths and weaknesses. It is good for personal and professional development. Individuals can make informed decisions about career paths, job changes, or further education. It enhances their prospects in the job market. It helps you recognize threats for proactive risk management. Individuals can prepare for potential challenges. Moreover, this analysis helps in skill development. It can highlight areas for improvement and guide targeted learning efforts. They can set realistic and achievable personal and professional objectives.
How to do a SWOT Analysis?
There are a few steps that are very important in the process. Here’s how to do a SWOT analysis:
- Gather your team together.
- Set up your quadrants on a whiteboard or projector.
- Start with strengths.
- Ask important questions.
- Follow suit with weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Organize the information collected into a neat document.
- Send out to the team with notes.
- Organize a second meeting to come up with action items and owners.
What are the four parts of a swot analysis?
One of the best tools for strategic planning is a SWOT analysis. You can find your Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. You can create a system for internal and external things that give success to an organization.
1. Strengths
Strengths are the internal attributes and resources. It supports a successful outcome. These are the positive factors within a business. It gives it an advantage over others.
- Strong brand reputation
- Skilled workforce
- Proprietary technology
- Loyal customer base
- Efficient supply chain
2. Weaknesses
Weaknesses are internal factors. It could hinder or damage the business’s performance. These are areas where the business needs improvement.
- Limited financial resources
- Poor location
- Lack of patent protection
- Weak brand presence
- Inefficient processes
3. Opportunities
Opportunities are external factors. The business can exploit this to its advantage. These are favorable situations or trends in the external environment. It could be leveraged for growth and success.
- Emerging markets
- Technological advancements
- Changes in consumer preferences
- Strategic partnerships
- Regulatory changes favoring the industry
4. Threats
Threats are external factors that cause trouble for the business. These are unfavorable trends or developments. It might pose challenges or risks to the business’s success.
- Economic downturns
- Increased competition
- Changes in regulations
- Shifts in consumer behavior
- Supply chain disruptions
Why Is SWOT Analysis Used?
1. Comprehensive Overview
SWOT analysis provides a thorough examination of an organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses, along with external opportunities and threats. This comprehensive overview enables businesses to understand their current position within the market and the factors that may influence their success or failure.
2. Strategic Planning
By identifying and analysing key factors that affect an organization, SWOT analysis is essential for strategic planning. It helps in setting objectives, formulating strategies, and determining the actions needed to achieve the desired goals.
3. Resource Allocation
SWOT analysis aids in the effective allocation of resources by highlighting areas that require investment and those that can be optimized. This ensures that resources are directed towards initiatives that offer the most significant potential for growth and success.
4. Competitive Advantage
Understanding both internal and external factors through SWOT analysis enables organizations to leverage their strengths and address weaknesses. This, in turn, helps them to gain a competitive edge over rivals by capitalizing on opportunities and mitigating threats.
5. Risk Management
SWOT analysis helps in identifying potential risks and challenges that could impact an organization’s success. By being aware of these risks, businesses can develop strategies to manage or avoid them, thereby reducing the likelihood of negative outcomes.
6. Decision-Making Framework
The structured approach of SWOT analysis provides a clear framework for decision-making. By assessing various factors systematically, organizations can make informed choices that align with their strategic goals.
7. Enhanced Communication
SWOT analysis facilitates communication within an organization by clearly outlining the factors that affect the business. This shared understanding among team members fosters collaboration and ensures everyone is aligned with the company’s objectives.
8. Identifying Growth Opportunities
SWOT analysis helps businesses identify and capitalize on growth opportunities. By understanding market trends and gaps, companies can develop strategies to expand their offerings or enter new markets, driving business growth.
9. Improving Organizational Performance
By focusing on strengths and addressing weaknesses, SWOT analysis can lead to improved performance. Organizations can enhance their processes, products, and services, leading to better efficiency and effectiveness.
10. Fostering Innovation
SWOT analysis encourages innovative thinking by challenging organizations to think creatively about how to address their weaknesses and exploit opportunities. This can lead to the development of new products, services, or business models, fostering a culture of innovation.
What Are the Pros and Cons of SWOT Analysis?
Pros:
- Problem Domain: SWOT analysis can evaluate products, partnerships, supply sources, business processes, markets, or technology implementations.
- Application Neutrality: SWOT analysis is suitable for strategic planning, opportunity analysis, competitive analysis, business development, or product development.
- Multi-Level Analysis: SWOT analysis helps identify necessary adjustments or strategies based on internal and external factors.
- Data Integration: SWOT analysis enhances enterprise-level planning, decision-making, communication, and operational coordination.
- Simplicity: SWOT analysis aggregates individual knowledge into collective group judgments.
- Cost: SWOT analysis is cost-effective. It is relatively simple and quick to perform.
Cons:
- No Weighting Factors: SWOT analysis makes it difficult to determine the impact of each factor.
- Ambiguity: SWOT analysis increases sales but also costs.
- Subjective Analysis: SWOT analysis can impact the reliability and relevance of the conclusions.
Do’s and Dont’s
Do’s:
- Collaborate with diverse stakeholders.
- Align strengths with market opportunities.
- Incorporate SWOT findings in strategic planning.
- Regularly review and update the SWOT analysis.
Dont’s:
- Avoid overlooking internal weaknesses.
- Don’t solely rely on historical data.
- Avoid overemphasizing a single factor.
- Don’t disregard emerging market trends and shifts.
Conclusion
A SWOT analysis provides comprehensive factors. It affects an organization. They can make plans for the future, and effectively allocate resources. SWOT analyses make sure that strategies remain relevant. It leads to sustained success and growth.
FAQ’s
Q1: What is SWOT Analysis?
A1: SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate an organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. It provides a structured approach to understanding the key factors that influence business performance and decision-making.
Q2: What does each component of SWOT stand for?
A2: SWOT stands for:
- Strengths: Internal attributes that give the organization a competitive advantage.
- Weaknesses: Internal factors that may hinder an organization’s success.
- Opportunities: External conditions that could be exploited to benefit the organization.
- Threats: External factors that could pose challenges to the organization’s success.
Q3: Why is SWOT Analysis important for businesses?
A3: SWOT Analysis is important because it helps businesses identify their current position in the market, recognize potential risks and opportunities, and develop strategic plans to achieve their goals. It aids in resource allocation, risk management, and gaining a competitive edge.
Q4: How is a SWOT Analysis conducted?
A4: A SWOT Analysis is conducted by gathering a team of stakeholders to brainstorm and evaluate the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Each component is analysed systematically, often using a matrix format, to develop strategies that align with the organization’s objectives.
Q5: Can SWOT Analysis be used for individual projects or personal development?
A5: Yes, SWOT Analysis can be applied to individual projects, personal development, or any situation that requires a strategic assessment. It helps in understanding the internal and external factors that can impact success and in making informed decisions.
Q6: How often should an organization conduct a SWOT Analysis?
A6: An organization should conduct a SWOT Analysis periodically, such as annually or biannually, or whenever there is a significant change in the market environment or the organization itself. Regular analysis ensures that the business remains responsive to internal and external changes.
Q7: What are the limitations of SWOT Analysis?
A7: The limitations of SWOT Analysis include its reliance on subjective input, the potential for oversimplification, and the risk of focusing too much on the analysis rather than on actionable strategies. It should be used as a guide rather than a definitive solution.
Q8: How does SWOT Analysis differ from other strategic planning tools?
A8: SWOT Analysis differs from other tools like PESTLE or Porter’s Five Forces in that it provides a simple yet comprehensive framework for evaluating both internal and external factors. While other tools may focus on specific areas, SWOT offers a balanced overview that integrates various aspects of the business environment.
Q9: What are some examples of strengths in a SWOT Analysis?
A9: Examples of strengths might include a strong brand reputation, a skilled workforce, proprietary technology, or a loyal customer base. These are internal factors that give the organization an advantage over competitors.
Q10: How can organizations use the results of a SWOT Analysis?
A10: Organizations can use the results of a SWOT Analysis to inform their strategic planning, prioritize initiatives, allocate resources effectively, and make informed decisions. By addressing weaknesses, leveraging strengths, exploiting opportunities, and mitigating threats, businesses can enhance their performance and achieve their objectives.