SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning tool used to evaluate an organization’s internal and external factors. It helps companies identify their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The acronym “SWOT” stands for:
- Strengths: Internal capabilities that give the company an advantage.
- Weaknesses: Internal factors that put the business at a disadvantage.
- Opportunities: External factors that the company can capitalize on to grow or improve.
- Threats: External challenges that may negatively impact the business.
SWOT Analysis serves as a powerful tool to make informed decisions, enhance strategies, and achieve business objectives. It’s widely used to evaluate a company’s current position and determine its future direction.
1. In a SWOT Analysis, What Are Opportunities?
Opportunities in a SWOT Analysis refer to external factors that a company can leverage for growth, profit, and expansion. These are favorable conditions that, if taken advantage of, can significantly impact a business’s success. Opportunities can arise from market trends, technological advances, economic changes, or shifts in customer needs.
Opportunities help companies determine strategic directions and identify ways to stay ahead of competitors. They are often seen as openings that allow a business to achieve its goals, capture market share, and boost revenue.
2. Overview of SWOT Components: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats
To understand how opportunities fit into the bigger picture, let’s briefly overview the components of SWOT:
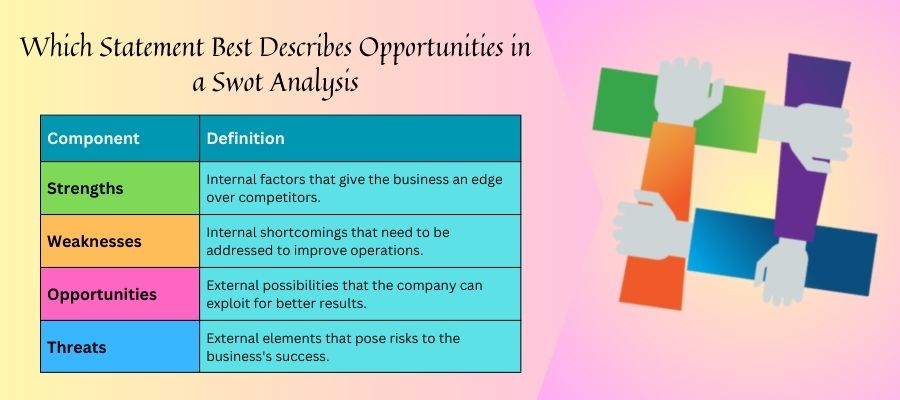
| Component | Definition |
|---|---|
| Strengths | Internal factors that give the business an edge over competitors. |
| Weaknesses | Internal shortcomings that need to be addressed to improve operations. |
| Opportunities | External possibilities that the company can exploit for better results. |
| Threats | External elements that pose risks to the business’s success. |
3. Which Statement Best Describes Opportunities in a SWOT Analysis?
The statement that best describes opportunities in a SWOT Analysis is:
“Opportunities are external factors that present potential growth or improvement for a company, allowing it to enhance performance, expand market presence, or increase profits.”
Opportunities differ from strengths, which are internal. While strengths are about what the company already excels at, opportunities are about what the company could do better by leveraging external situations.
4. Identifying Opportunities
A. Techniques for Recognizing Opportunities
Recognizing opportunities requires a strategic mindset and the use of specific techniques:
- Market Analysis: Evaluate market trends, customer needs, and emerging demands to find areas for expansion or new product development.
- Competitor Analysis: Study competitors to understand gaps in the market and areas where your business can gain an advantage.
- Customer Feedback: Collect and analyze customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and unmet customer needs.
- SWOT Workshops: Organize brainstorming sessions with team members to discuss potential opportunities and ideas.
- SWOT Matrix: Use a SWOT matrix to visualize and categorize opportunities based on their impact and feasibility.
B. Tools and Frameworks to Aid in Opportunity Identification
To make the identification of opportunities more structured, you can use the following tools and frameworks:
- PEST Analysis: A tool to analyze Political, Economic, Social, and Technological factors influencing the market.
- Porter’s Five Forces: Helps in understanding the competitive landscape by examining industry forces such as competition, supplier power, and buyer power.
- Customer Journey Mapping: Understand customer interactions with your product or service to find touchpoints for enhancement.
- Market Segmentation Analysis: Identify specific segments in the market that have growth potential.
5. Examples of Opportunities
A. Case Studies from Various Industries
Here are some examples of opportunities from different industries:
- Technology Sector: A software company identified an opportunity to create a cloud-based solution as more businesses moved to remote work. This led to significant revenue growth.
- Retail Industry: A clothing brand saw a chance to enter the sustainable fashion market, leading to a new line of eco-friendly products.
- Healthcare: A pharmaceutical company recognized a rising demand for telemedicine services, launching a digital health platform that attracted a wider audience.
B. Real-World Applications of Opportunity Identification
Case Study – Netflix: Netflix identified an opportunity to move from DVD rentals to a streaming service. By leveraging advancements in internet speeds and changes in viewing habits, Netflix transformed itself into a market leader in the entertainment industry.
Case Study – Tesla: Tesla identified the opportunity to focus on electric vehicles when the market was still dominated by traditional fuel cars. By doing so, it captured a significant portion of the electric car market and became a major player in the automotive industry.
Also Read: What Are the Four Parts of a Swot Analysis?
6. Best Practices for Opportunity Analysis
A. Recommendations for Conducting Effective Opportunity Analysis
To effectively analyze opportunities:
- Use Data-Driven Insights: Utilize data and statistics to support your analysis. This includes sales data, customer behavior, and industry trends.
- Prioritize Opportunities: Not all opportunities are worth pursuing. Use criteria like feasibility, potential ROI, and alignment with company goals to prioritize them.
- Monitor Competitors: Keep an eye on competitors’ actions to identify gaps in the market that your company can fill.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve employees, customers, and industry experts in the opportunity analysis process. This provides a comprehensive view of potential opportunities.
- Perform a SWOT Analysis Regularly: Markets evolve, and so do opportunities. Conduct a SWOT analysis frequently to stay up-to-date.
B. Importance of Continuous Monitoring and Reassessment
Markets change, and opportunities can quickly turn into threats if not acted upon in time. Continuous monitoring helps companies:
- Adapt to market changes.
- Adjust strategies to meet current demands.
- Avoid potential risks by being proactive.
- Stay ahead of competitors.
Reassessing opportunities ensures that the company remains relevant and aligned with its goals.
Conclusion
Opportunities are a crucial aspect of a SWOT Analysis. They represent external chances for a business to grow, innovate, and excel. By effectively identifying and capitalizing on opportunities, companies can gain a competitive advantage and strengthen their market position. It’s essential to use reliable tools and techniques, engage stakeholders, and continuously monitor the market to stay ahead.
FAQ
What Are Opportunities in SWOT Analysis?
Opportunities are external factors that can positively impact a business, allowing it to improve performance, capture new markets, or increase profits.
Which Statement Best Describes Opportunities in a SWOT Analysis?
Opportunities are the external factors that present potential for growth or improvement. They allow a company to take advantage of market conditions and stay competitive.
How Are Opportunities Different from Strengths in a SWOT Analysis?
Strengths are internal factors the company already possesses, like skills or resources. Opportunities are external conditions that the company can exploit to its advantage.
How Should Opportunities Be Used in a Strategic Plan?
Opportunities should be prioritized based on their feasibility and potential impact. Integrate them into the strategic plan by aligning them with the company’s goals and resources.
How Often Should Opportunities in a SWOT Analysis Be Reviewed?
It is recommended to review opportunities quarterly or whenever there is a significant market shift. This helps in keeping the strategic plan relevant and effective.